A standard seasonal respiratory virus that usually infects school-aged kids is inflicting an unusually massive spike in instances throughout Europe and the US this summer time. The surge in transmission is a big hazard to sure susceptible populations together with pregnant individuals, in line with a well being alert launched by the Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention on Tuesday.
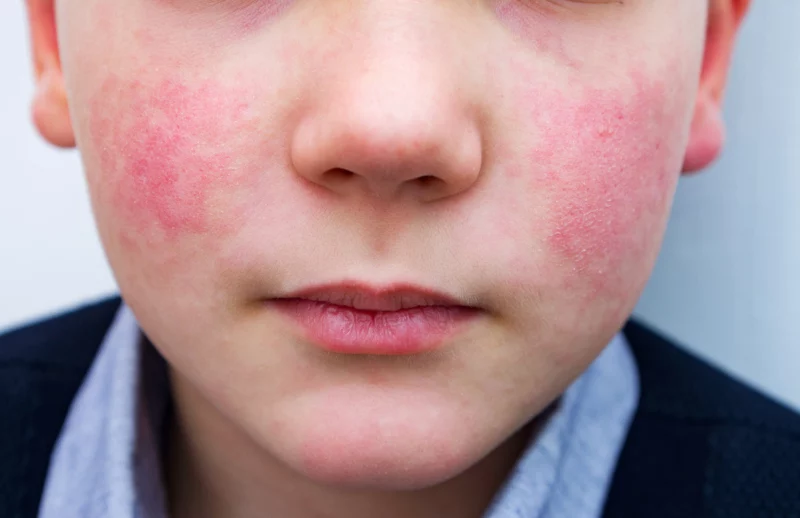
The virus is parvovirus B19, aka B19V, which spreads by way of respiratory droplets and usually causes a light, two-phased sickness in kids. The primary section is marked by flu-like signs that may embody fever, headache, malaise, muscle aches, cough, sore throat, and joint ache. Within the second section, a attribute “slapped cheek” rash develops, which can also be known as Fifth Illness or Erythema Infectiosum. By age 20, about 50 p.c of individuals have been contaminated and have antibodies that may assist combat reinfection. And by age 40, the determine rises to 70 p.c.
However, for individuals who have compromised immune programs, are pregnant, or have sure circumstances, resembling sickle cell anemia, the virus may cause extreme problems, resembling extreme anemia, myocarditis, hepatitis, or encephalitis. In being pregnant, the virus can infect the fetus and trigger harmful problems and miscarriage.
Often, the virus spreads with little discover, inflicting extreme illness solely hardly ever. However, in latest months, B19V has risen above the din of seasonal viruses. On the finish of final 12 months, as an illustration, well being researchers in Israel reported the nation’s largest and longest B19V outbreak thus far, with the speed of instances rising ninefold over the speed between 2020 and 2022, and 6.6-fold over earlier years. Pregnant individuals noticed a relative improve in danger through the outbreak.
Worldwide surge
In June, researchers in Denmark reported a peak in instances earlier this 12 months that was the best charge of an infection up to now 10 years, 3.5-fold greater than the subsequent highest peak from 2017. However Denmark just isn’t alone. Additionally in June, the European Centre for Illness Prevention and Management reported that 14 European nations have seen unusually massive will increase in B19V infections.
In response to the US CDC, the surge appeared to reach in North America in June, although the information is restricted. Given its usually delicate presentation, B19V just isn’t a nationally notifiable an infection within the US, which means instances aren’t tracked. Nonetheless, the CDC does passively accumulate knowledge on the virus.
For example, business laboratories have reported a rise in take a look at positivity, and the proportion of individuals with IgM antibodies—an indicator of latest an infection—elevated amongst all ages from lower than 3 p.c between 2022 and 2024 to 10 p.c this June. Youngsters between the ages of 5 and 9 noticed the best improve, going from 15 p.c between 2022 and 2024 to 40 p.c in June 2024. Amongst plasma donors, the prevalence of pooled samples with a threshold stage of B19V DNA went from 1.5 p.c in December 2023 to twenty p.c in June 2024. The CDC additionally stated it has gotten anecdotal experiences of will increase in instances of B19V in pregnant sufferers.
The CDC requires clinicians to be extra conscious of the potential for B19V infections. For pregnant individuals and others at excessive danger, the CDC recommends taking precautions, like masking and vigilant hand hygiene. That is significantly necessary for any high-risk individuals in work settings that contain shut contact with kids, resembling faculties and daycares, the CDC notes.
It is unclear what’s driving the B19V, however researchers have famous that B19V tends to have small surges each three to 4 years. With the worldwide debut of SARS-CoV-2 on the finish of 2019, many seasonal and cyclical patterns of infectious illnesses had been disrupted, inflicting uncommon dips and spikes in transmission. B19V transmission might have likewise been affected.

