Part two of Google’s mobile-first indexing – rendering – is Chrome and has been since 2018, in response to search engine optimisation skilled Cindy Krum. In a newly launched video presentation, Krum stated:
- “What I consider is occurring right here is that Google failed to inform us right now in 2018, when it launched, that what they have been utilizing for the second part of indexing was not a bot, per se. It was our personal computer systems in our houses. Your Chrome getting used as a rendering useful resource turned obtainable. Meaning you. As somebody requested the positioning and executed the JavaScript, they might go and fetch that from their laptop. They wouldn’t use their bot to render it. They’d wait till a person rendered the web page for them after which they might simply go seize that full-page render in order that they might course of it.
- “… Google [is] utilizing our personal computer systems to pre-process info for indexing and our personal browsers to seize info and rendering. We haven’t essentially opted into this and we’re not knowingly getting something again.
- “…Google can also be utilizing our rendering information and our conduct – by way of making fashions like cohort fashions and matter fashions, historical past and engagement fashions – they usually’re utilizing this all taking it from our native computer systems with out permission and passing it as much as their processors. Now it’s pre-processed domestically in order that it may be batched and despatched up after which sending it to their algorithms to be additional processed and evaluated. That’s how they’re in a position to get the rankings that they do, but in addition that’s how they’re in a position to perceive issues like demographic cohorts, Journeys, the place you store, and make selections and understanding and modeling that in order that they will use that information of their promoting fashions in PMax, in PPC campaigns. They’re utilizing our personal conduct to market to us and to coach AI that serves advertisements to do a greater job.”
Put merely in two slides:
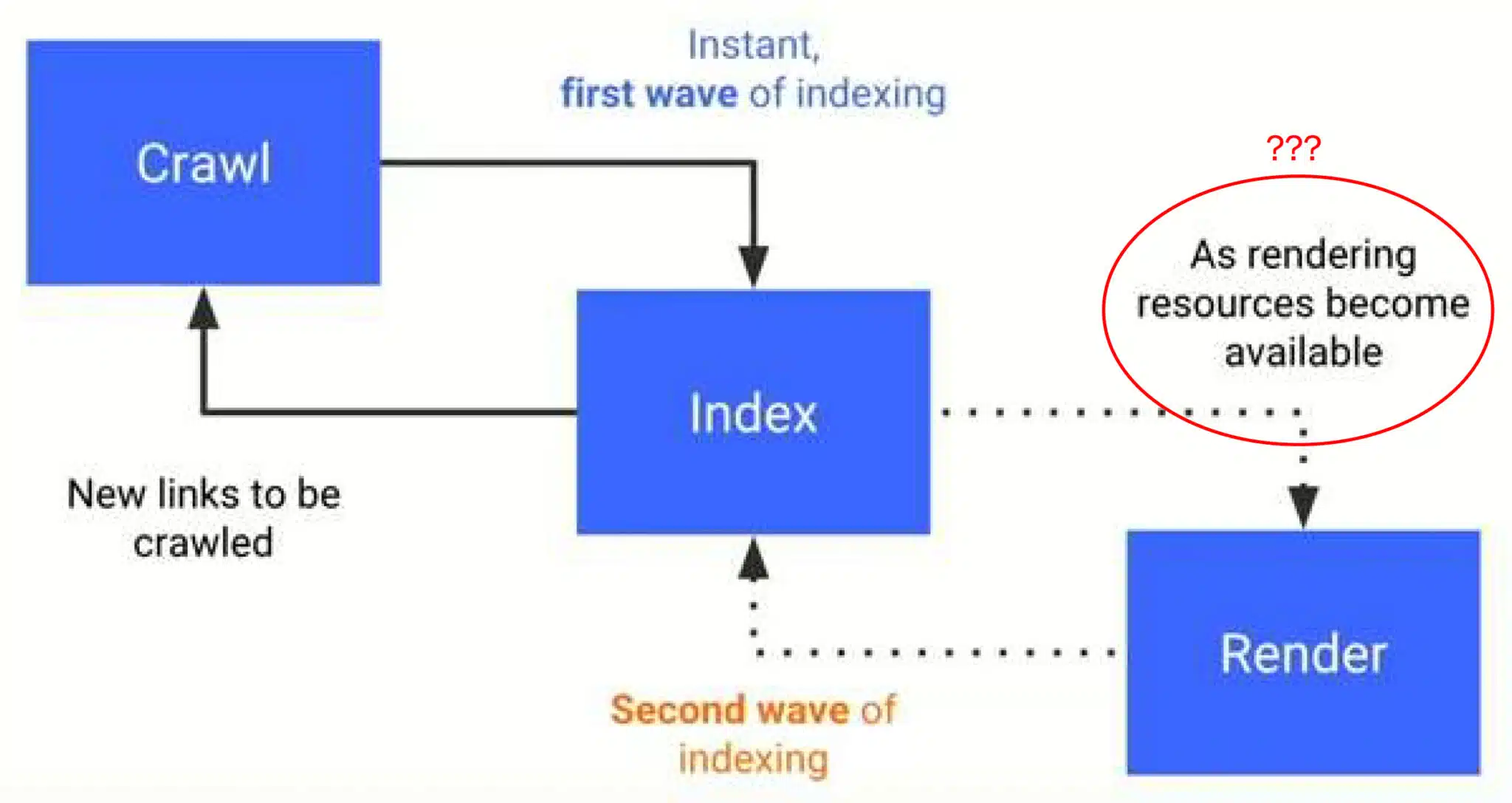

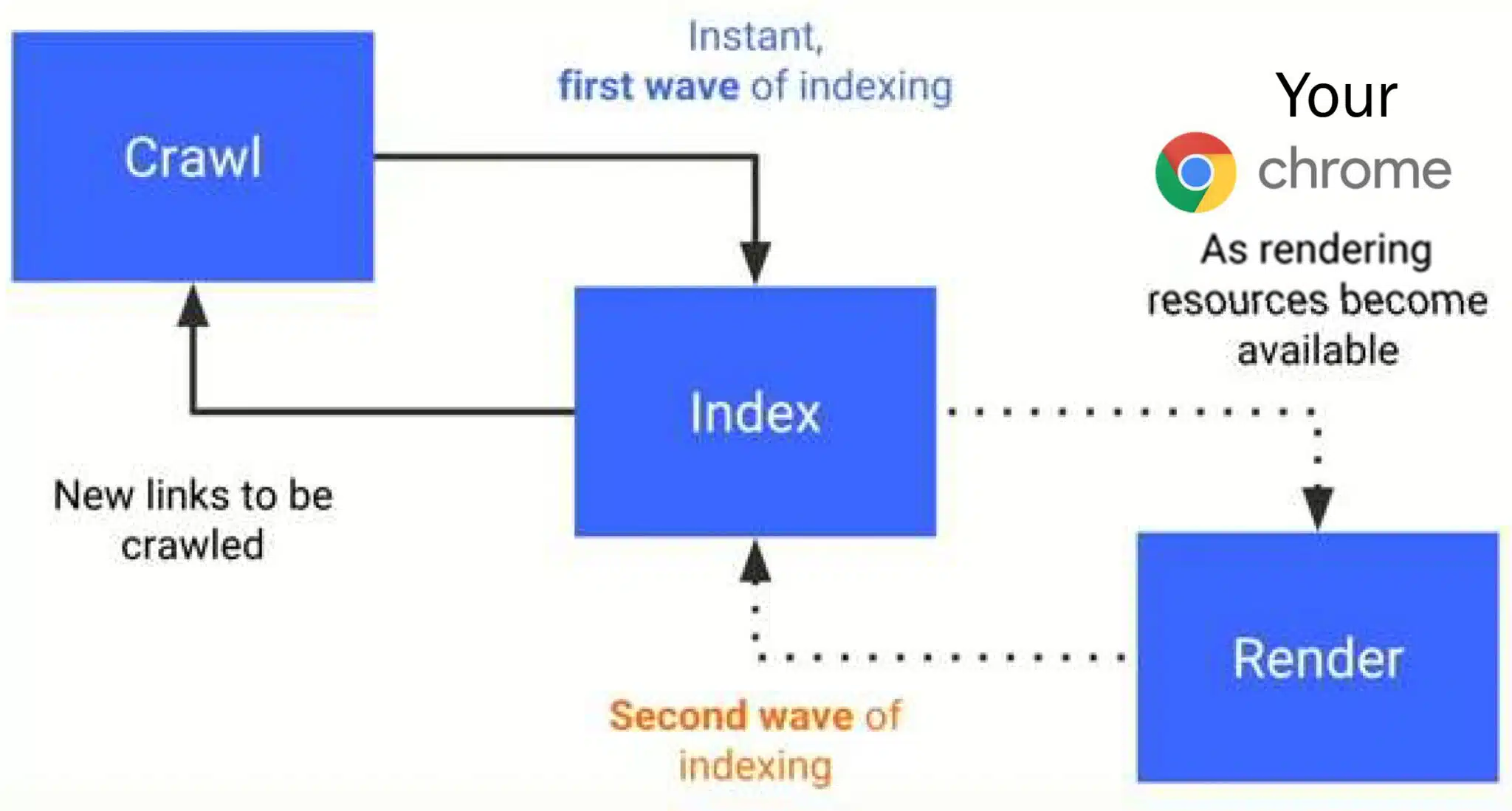

Connecting dots. There are a number of claims made about different big implications of Google’s change to mobile-first indexing in Krum’s presentation, in addition to how Chrome primarily fuels Google’s unlawful search monopoly:
- Person computer systems as sources: Google makes use of customers’ units to render and course of JavaScript, which they then index – primarily outsourcing computational work to customers. Primarily, Google is utilizing Chrome in the identical method your laptop might be used for Bitcoin mining.
- Core Internet Vitals: Google captures actual person information to evaluate web page load efficiency and interplay and feeds this information into its rating algorithms.
- Browser updates and information assortment: Frequent Chrome updates guarantee information assortment aligns with Google’s search and advert fashions, contributing to focused promoting and AI coaching.
- Privateness violations: Google has been discovered indexing personal information (e.g., personal WhatsApp teams), possible resulting from its aggressive caching and information assortment practices.
- Chrome’s position in AI: AI may be very costly, so Google may use Chrome’s processing mannequin to assist with AI growth, giving them an edge within the AI arms race.
- Advert monitoring and focusing on: Google’s information assortment extends into promoting fashions like cohort focusing on and person conduct modeling for advert optimization.
- Cookies and privateness: Regardless of promising to finish third-party cookies, Google continues to make use of them for intensive monitoring and information assortment.
Doable search engine optimisation implications. I reached out to Krum and requested her what the potential search engine optimisation implications are right here if all of that is right. She instructed me:
- If a web page has hyperlinks that by no means get clicked, Google is much less more likely to crawl it. We knew this, in idea, however now we now have a greater concept of the way it works.
- Actual person engagement is probably going factoring in additional than beforehand thought – we now have identified this because the Google Search leak.
- Manipulation of SERP and click on info is a big vulnerability, if it occurs in Chrome.
- Precise person rendering is vital, so selective serving for GoogleBot may not be an incredible technique.
Why we care. We all know that Google collects intensive Chrome and end-user information from its different numerous companies (Search, YouTube, Adverts, and so on.). That stated, and to be clear, a lot of what she discusses is for now an unconfirmed idea (Krum does use the phrase “tinfoil” throughout her presentation and there are a number of “X-Information” themed slides).
Once I first watched the video, I discovered it equal elements fantastical, inconceivable and completely plausible. It’s quite a bit to course of. Nonetheless, in gentle of all of the revelations from the DOJ trial and the leak, nothing Krum discusses within the video looks like too wild of hypothesis. I’ll be curious to see whether or not Google responds.
Further studying. Krum additionally referenced analysis by Malte Ubl, a former Googler, who stated that “Google makes use of an up-to-date model of Chrome for rendering” and whose analysis discovered that “100% of HTML pages resulted in full-page renders, together with pages with advanced JS interactions.”
The presentation. Watch the video and resolve for your self (I counsel beginning round 6:37): Part II of Google’s Cell-First Indexing is simply Chrome.

