The human mind, with its intricate community of billions of neurons, consistently buzzes with electrical exercise. This neural symphony encodes our each thought, motion, and sensation. For neuroscientists and engineers engaged on brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), deciphering this complicated neural code has been a formidable problem. The issue lies not simply in studying mind alerts, however in isolating and decoding particular patterns amidst the cacophony of neural exercise.
In a big leap ahead, researchers on the College of Southern California (USC) have developed a brand new synthetic intelligence algorithm that guarantees to revolutionize how we decode mind exercise. The algorithm, named DPAD (Dissociative Prioritized Evaluation of Dynamics), provides a novel strategy to separating and analyzing particular neural patterns from the complicated mixture of mind alerts.
Maryam Shanechi, the Sawchuk Chair in Electrical and Laptop Engineering and founding director of the USC Middle for Neurotechnology, led the staff that developed this groundbreaking know-how. Their work, just lately printed within the journal Nature Neuroscience, represents a big development within the area of neural decoding and holds promise for enhancing the capabilities of brain-computer interfaces.
The Complexity of Mind Exercise
To understand the importance of the DPAD algorithm, it is essential to grasp the intricate nature of mind exercise. At any given second, our brains are engaged in a number of processes concurrently. For example, as you learn this text, your mind isn’t solely processing the visible info of the textual content but in addition controlling your posture, regulating your respiration, and probably serious about your plans for the day.
Every of those actions generates its personal sample of neural firing, creating a fancy tapestry of mind exercise. These patterns overlap and work together, making it extraordinarily difficult to isolate the neural alerts related to a particular habits or thought course of. Within the phrases of Shanechi, “All these completely different behaviors, resembling arm actions, speech and completely different inside states resembling starvation, are concurrently encoded in your mind. This simultaneous encoding provides rise to very complicated and mixed-up patterns within the mind’s electrical exercise.”
This complexity poses vital challenges for brain-computer interfaces. BCIs intention to translate mind alerts into instructions for exterior gadgets, probably permitting paralyzed people to regulate prosthetic limbs or communication gadgets by way of thought alone. Nonetheless, the flexibility to precisely interpret these instructions relies on isolating the related neural alerts from the background noise of ongoing mind exercise.
Conventional decoding strategies have struggled with this process, usually failing to differentiate between intentional instructions and unrelated mind exercise. This limitation has hindered the event of extra subtle and dependable BCIs, constraining their potential functions in medical and assistive applied sciences.
DPAD: A New Method to Neural Decoding
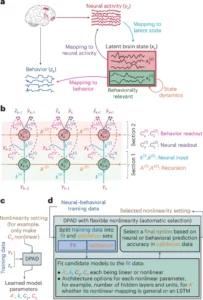
The DPAD algorithm represents a paradigm shift in how we strategy neural decoding. At its core, the algorithm employs a deep neural community with a singular coaching technique. As Omid Sani, a analysis affiliate in Shanechi’s lab and former Ph.D. pupil, explains, “A key factor within the AI algorithm is to first search for mind patterns which are associated to the habits of curiosity and be taught these patterns with precedence throughout coaching of a deep neural community.”
This prioritized studying strategy permits DPAD to successfully isolate behavior-related patterns from the complicated mixture of neural exercise. As soon as these main patterns are recognized, the algorithm then learns to account for remaining patterns, making certain they do not intrude with or masks the alerts of curiosity.
The pliability of neural networks within the algorithm’s design permits it to explain a variety of mind patterns, making it adaptable to numerous varieties of neural exercise and potential functions.
Supply: USC
Implications for Mind-Laptop Interfaces
The event of DPAD holds vital promise for advancing brain-computer interfaces. By extra precisely decoding motion intentions from mind exercise, this know-how might significantly improve the performance and responsiveness of BCIs.
For people with paralysis, this might translate to extra intuitive management over prosthetic limbs or communication gadgets. The improved accuracy in decoding might enable for finer motor management, probably enabling extra complicated actions and interactions with the surroundings.
Furthermore, the algorithm’s potential to dissociate particular mind patterns from background neural exercise might result in BCIs which are extra strong in real-world settings, the place customers are consistently processing a number of stimuli and engaged in varied cognitive duties.
Past Motion: Future Purposes in Psychological Well being
Whereas the preliminary focus of DPAD has been on decoding movement-related mind patterns, its potential functions prolong far past motor management. Shanechi and her staff are exploring the potential for utilizing this know-how to decode psychological states resembling ache or temper.
This functionality might have profound implications for psychological well being therapy. By precisely monitoring a affected person’s symptom states, clinicians might achieve worthwhile insights into the development of psychological well being situations and the effectiveness of remedies. Shanechi envisions a future the place this know-how might “result in brain-computer interfaces not just for motion issues and paralysis, but in addition for psychological well being situations.”
The power to objectively measure and monitor psychological states might revolutionize how we strategy customized psychological well being care, permitting for extra exact tailoring of therapies to particular person affected person wants.
The Broader Impression on Neuroscience and AI
The event of DPAD opens up new avenues for understanding the mind itself. By offering a extra nuanced means of analyzing neural exercise, this algorithm might assist neuroscientists uncover beforehand unrecognized mind patterns or refine our understanding of recognized neural processes.
Within the broader context of AI and healthcare, DPAD exemplifies the potential for machine studying to sort out complicated organic issues. It demonstrates how AI might be leveraged not simply to course of present information, however to uncover new insights and approaches in scientific analysis.



