Meta’s latest choice to maneuver from fact-checkers to a neighborhood notes mannequin akin to X, highlights a rising divide in how digital platforms deal with free speech and content material moderation. This underscores a deeper disconnect throughout digital channels. These divergent approaches to moderation, mixed with escalating information privateness issues, pose important challenges for entrepreneurs and shoppers.
On the coronary heart of this lies a crucial rigidity: How can we steadiness the rules of free speech with the necessity for belief and accountability? How can client calls for for information privateness coexist with the realities of efficient digital advertising and marketing? These unresolved questions underscore a rift that might essentially reshape the way forward for digital advertising and marketing and on-line belief.
Background: A timeline
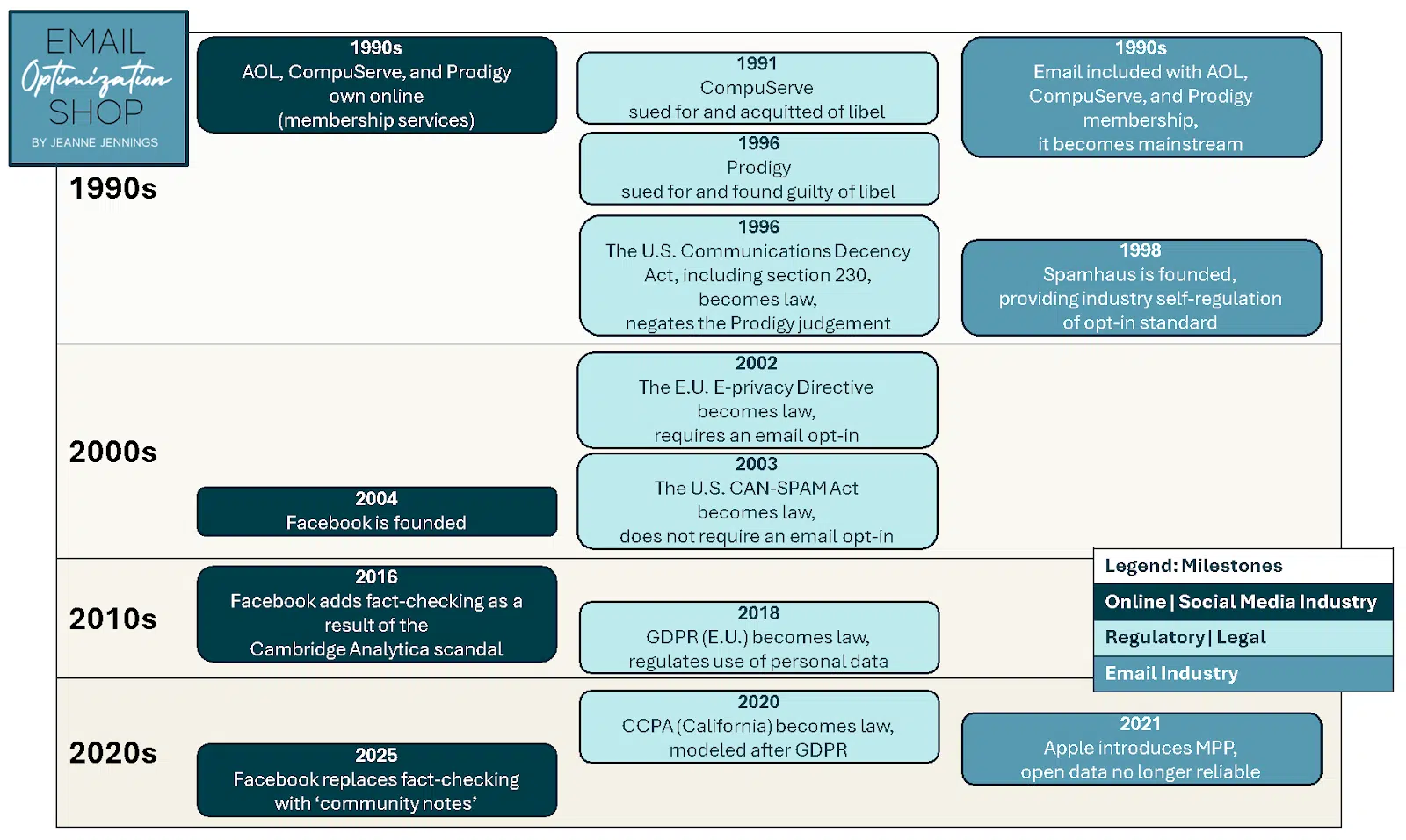
To know the present state of affairs, it’s useful to evaluation how we received right here. Under is a timeline of milestones throughout social media, electronic mail advertising and marketing and regulatory/authorized/restrictive occasions because the Nineties.
CompuServe, Prodigy, Meta and Part 230
Within the early Nineties, on-line platforms like CompuServe and Prodigy confronted crucial authorized challenges over user-generated content material. CompuServe was acquitted of libel in 1991 on the grounds that it acted as a impartial distributor of content material, very like a soapbox in a public sq.. Prodigy, nonetheless, was discovered liable in 1996 as a result of it proactively moderated content material, positioning itself extra like a writer.
To deal with these contradictory rulings and protect web innovation, the U.S. authorities handed the Communications Decency Act of 1996, together with Part 230, which shields platforms from legal responsibility for user-generated content material. This enables platforms like Fb (based in 2004) to thrive with out worry of being handled as publishers.
Quick-forward to 2016, when Fb confronted public scrutiny over its position within the Cambridge Analytica scandal. On the time, CEO Mark Zuckerberg acknowledged the platform’s accountability and launched fact-checking to fight misinformation.
But in 2025, Meta’s new coverage shifts accountability for content material moderation again to customers, citing Part 230 protections.
E-mail advertising and marketing, blocklists and self-regulation
E-mail advertising and marketing, one of many earliest digital channels, took a distinct path. By the late Nineties, spam threatened to overwhelm inboxes, prompting the creation of blocklists like Spamhaus (1998). This allowed the business to self-regulate successfully, preserving electronic mail as a viable advertising and marketing channel.
The CAN-SPAM Act of 2003 set baseline requirements for industrial electronic mail, equivalent to requiring unsubscribe choices. Nonetheless, it fell wanting the proactive opt-in necessities mandated by the EU’s 2002 e-privacy directive and the U.S. blocklist suppliers. E-mail entrepreneurs largely embraced opt-in requirements to construct belief and shield the channel’s integrity, and the business continued to depend on blocklists in 2025.
GDPR, CCPA, Apple MPP and client privateness
Rising client consciousness about information privateness led to landmark rules just like the EU’s Basic Information Safety Regulation (GDPR) in 2018 and California’s Client Privateness Act (CCPA) in 2020. These legal guidelines gave shoppers higher management over their private information, together with the suitable to know what information is collected, how it’s used, have it deleted and opt-out of its sale.
Whereas GDPR requires express consent earlier than information assortment, CCPA gives fewer restrictions however emphasizes transparency. These rules posed challenges for entrepreneurs reliant on customized concentrating on, however the business is adapting. Social platforms, nonetheless, proceed to depend on implicit consent and broad information insurance policies, creating inconsistencies within the consumer expertise.
Then in 2021, Apple launched mail privateness safety (MPP), which made electronic mail open charge information unreliable.
Dig deeper: U.S. state information privateness legal guidelines: What it’s worthwhile to know
Concerns
Client issues and trade-offs
As shoppers more and more demand management over their information, they’re typically unaware of the trade-off: much less information means much less customized and fewer related advertising and marketing. This paradox leaves entrepreneurs in a difficult place, balancing privateness with efficient outreach.
The worth of moderation: Classes from electronic mail advertising and marketing and different social media platforms
With out blocklists like Spamhaus, electronic mail would have devolved right into a cesspool of spam and scams, rendering the channel unusable. Social media platforms face an identical dilemma. Truth-checking, whereas imperfect, is crucial for sustaining belief and usefulness, particularly in an period the place misinformation erodes public confidence in establishments.
Likewise, platforms like TikTok and Pinterest appear to keep away from these controversies over moderation. Are they much less politically charged, or have they developed more practical fact-checking methods? Their approaches supply potential classes for Meta and others.
Expertise as an answer, not an impediment
Meta’s issues about false positives in fact-checking mirror challenges electronic mail entrepreneurs confronted up to now. AI and machine studying developments have considerably improved electronic mail spam filtering, lowering errors and preserving belief. Social platforms might undertake related applied sciences to reinforce content material moderation slightly than retreating from the accountability.
Dig deeper: Entrepreneurs, it’s time to stroll the stroll on accountable media
The larger image: What’s at stake?
Think about a social media platform overwhelmed by misinformation as a result of insufficient moderation, mixed with irrelevant advertising and marketing messages stemming from restricted information brought on by strict privateness insurance policies. Is that this the sort of place the place you’d select to spend your time on-line?
Misinformation and privateness issues increase crucial questions on the way forward for social media platforms. Will they lose consumer belief, as X did after its rollback of content material moderation? Will platforms that average solely probably the most egregious misinformation change into echo chambers of unverified content material? Will lack of relevance have a unfavourable affect on digital advertising and marketing high quality and income on these platforms?
Fixing the disconnect
Listed here are some actionable steps that may assist reconcile these competing priorities and guarantee a extra cohesive digital ecosystem:
- Unified requirements throughout channels: Set up baseline privateness and content material moderation requirements throughout digital advertising and marketing channels.
- Proactive client training: Educate customers about how information and content material are managed throughout platforms and on the professionals and cons of strict information privateness necessities. Give shoppers the data and greater than all-or-nothing choices on information privateness.
- Use AI for moderation: Put money into expertise to reinforce accuracy and cut back errors in content material moderation.
- Encourage international regulatory alignment: Preemptively align with stricter privateness legal guidelines like GDPR to future-proof operations. The U.S. Congress has not succeeded on this, even because the states are passing legal guidelines on these points.
To make sure the way forward for social digital areas, we should tackle the challenges of free speech and information privateness. This requires collaboration and innovation throughout the business to construct belief with customers and proceed to supply a constructive on-line expertise in all channels.
Dig deeper: The right way to steadiness ROAS, model security and suitability in social media promoting
Contributing authors are invited to create content material for MarTech and are chosen for his or her experience and contribution to the martech neighborhood. Our contributors work below the oversight of the editorial employees and contributions are checked for high quality and relevance to our readers. The opinions they categorical are their very own.

