College students have to reveal their competencies in areas past conventional classroom assessments. In an period of superior applied sciences and synthetic intelligence, the usage of these instruments in training raises issues about its affect on pupil studying, significantly on the subject of assessments. When finishing assignments or making ready for exams, there’s a concern that they may be “faking it till they make it.” Because of this as an alternative of genuinely understanding the fabric, college students might merely carry out nicely on assessments as a result of they’ve entry to AI instruments that assist them produce right solutions with out deeply studying the ideas. We argue that educators have to attempt to offer extra genuine studying experiences that don’t simply lend themselves to the usage of superior applied sciences. A method to do that is by offering experiential studying alternatives for college students to reveal their competencies in a extra real-world setting. This may be revealing for educators as they see a special facet to college students exploring and making use of course content material in genuine methods. The aim of this text is to offer issues for educators when creating experiential studying alternatives for college students. Though the concepts introduced on this article stem from a steady subject of exploration in greater training, (see Beard & Wilson, 2006; Cantor, 1995; Finely & Bowen, 2021; Tormey, 2022 for additional analysis), this text summarizes our studying and interpretations when creating experiential studying alternatives for our college students.
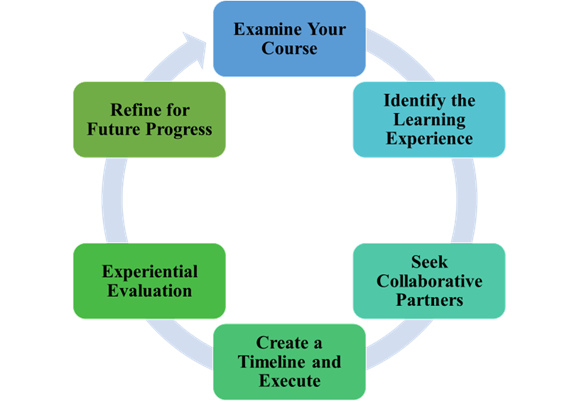
Consideration 1: Study Your Course
The primary consideration in creating an experiential studying alternative is to evaluate the scholar studying outcomes (SLOs) on your course, paying particular consideration to the outcomes which might be troublesome to evaluate with conventional strategies. Think about which outcomes college students typically battle to satisfy, specific frustration over, or the place you’re feeling the present assessments don’t totally seize their efficiency. Replicate on whether or not there are college students who carry out nicely on assessments, however based mostly on their actions at school, you might have issues about how they’d carry out in real-world situations. As an example, is there a quiet pupil who excels in written assignments however struggles with a course end result tied to public talking? Subsequent, think about the content material college students have to grasp, the depth of their understanding, and the talents they should apply that data in sensible conditions.
Consideration 2: Establish the Studying Expertise
After reflecting in your course design, the second consideration is to establish the kind of expertise you need college students to interact in that may assist bridge the hole between principle and observe and decide how you’ll assess their success. These real-world experiences ought to allow college students to interact extra deeply with course content material whereas offering you with a possibility to evaluate their efficiency in a extra genuine method. Thus, it’s important that you simply establish the goals for the training expertise. For instance, you might assign college students to work with native companies or startups to develop a advertising plan or facilitate a lab challenge the place college students work with native environmental organizations to investigate water high quality or air air pollution. This is able to permit them to use particular ideas and theories, comparable to market segmentation, monetary forecasting, or chemical testing strategies in a real-world context. When it comes to evaluation, think about using a mix of statement, reflective journaling, and genuine utility of expertise. For instance, training college students may study a literacy technique at school after which apply it in an actual instructing context, with the reflective journal capturing their ideas on the effectiveness of the technique and the challenges they encountered. This method means that you can assess not simply what college students know, however how they apply their data in real-world conditions inside a supportive studying surroundings.
Consideration 3: Search Collaborative Companions
The third consideration is who to accomplice with. Collaborative companions can embody neighborhood companies, companies, authorities establishments, public establishments, and even on-campus collaborators, comparable to college entities. The objective is to contain the proper stakeholders—those that are decision-makers or have the affect wanted to make the collaboration significant. Following Covey (2013) precept of “Assume Win-Win” from his 7 Habits of Extremely Efficient Individuals, partnerships needs to be approached with the mindset of making mutually useful outcomes the place all events succeed collectively. Profitable collaborations are constructed on shared targets, complementary strengths, and clear communication. Covey’s (2013) “Search First to Perceive, Then to Be Understood” emphasizes the significance of understanding the wants and priorities of your companions earlier than asserting your personal. This mindset fosters deeper, extra empathetic connections, guaranteeing that each side are totally aligned within the goals of the experiential studying. To construct an efficient partnership, it’s essential to determine a win-win basis, the place every accomplice feels their contribution is valued and that they’re gaining one thing significant from the collaboration. Covey’s (2013) behavior “Synergize” focuses on leveraging the strengths of every social gathering to create one thing larger than the sum of its components. By combining the distinctive skills, sources, and views of every accomplice, you possibly can foster a robust, cooperative surroundings.
Consideration 4: Create a Timeline and Execute
The fourth consideration is establishing a sensible timeline that features the planning, implementation, and evaluation of the expertise. Planning the expertise needs to be intentional and can take time; due to this fact, it’s endorsed that the method is began at the least one semester previous to implementation. Moreover, clearly figuring out and articulating the roles and duties of every accomplice is significant. Every accomplice ought to perceive their function within the collaboration, what they’re accountable for, and the way their contributions will profit each themselves and the partnership as an entire. For instance, if a literacy course is partnered with an area college district to supply an afterschool program to youth, the varsity district might assume accountability for recruiting youth to take part whereas the instructor candidates would supply the literacy instruction. This readability, together with open strains of communication throughout implementation, ensures the longevity and success of the partnership. On the conclusion of the semester, evaluation should be carried out to judge the general expertise from every accomplice’s perspective. Companions want to satisfy to evaluate subsequent steps and focus on areas for program enchancment. A debriefing assembly needs to be held inside a couple of weeks of ending the expertise with a view to make mandatory changes earlier than a brand new implementation cycle.
Consideration 5: Experiential Analysis
The fifth consideration is to find out how you’ll consider the success of the expertise. Schon (1983) identifies two sorts of reflection: reflection in motion and reflection on motion. Reflection in motion refers to observing, considering, and responding to occasions that happen through the expertise permitting people to adapt and handle challenges in actual time. For instance, an accounting course has partnered with a company to help neighborhood members with tax submitting and has found that people have restricted English proficiency. By in motion reflection, companions can shortly reply by arranging language help and make sure the tax help continues easily. Moreover, reflection on motion requires gathering suggestions from companions by surveys, anecdotal data, and dialogue after the expertise to tell program enchancment. Referring to the accounting class instance, all concerned individuals needs to be requested to replicate on the expertise. Their suggestions can then be analyzed throughout a debriefing assembly to judge this system and establish mandatory adjustments for ongoing implementation.
Consideration 6: Refine for Future Progress
The ultimate consideration is to refine the expertise to make sure steady enchancment and future development. Information collected from assessments and evaluations needs to be analyzed to establish strengths, areas for enchancment, and insights that inform selections about future iterations of the expertise. School should think about the training expertise, particularly how it’s aligned to the course and if college students met the SLOs with success. Likewise, companions want to contemplate the sustainability of their involvement for ongoing implementation. This reflection course of is important for making changes that improve each pupil outcomes and the partnership transferring ahead.
Determine 1
Consideration Cycle
Conclusion
These issues have emerged from private experiences growing experiential studying alternatives for college students. We strongly encourage college to include extra genuine studying alternatives into their course design as a way to fight challenges posed by superior applied sciences. Partnerships have the facility to offer college students real-world studying that fosters deeper understanding and educational excellence.
Elizabeth Falzone, Ph.D., is an assistant professor of training at Niagara College.
Karen Poland, Ed.D., is an assistant professor of training at Niagara College.
References
Beard, C., & Wilson, J. P. (2006). Experiential studying: A greatest observe handbook for educators and trainers (2nd ed.). Kogan Web page.
Cantor, J. A. (1995). Experiential studying in greater training: Linking classroom and neighborhood (ASHE-ERIC Larger Training Report No. 7). ERIC Clearinghouse on Larger Training, Graduate Faculty of Training and Human Improvement, The George Washington College.
Covey, S. R. (2013). The 7 habits of extremely efficient individuals: Highly effective classes in private change. Simon & Schuster.
Finley, L. L., & Bowen, G. A. (2021). Experiential studying in greater training : points, concepts, and challenges for selling peace and justice. Data Age Publishing, Inc.
Schon, D. A. (1983) The reflective practitioner: How professionals assume in motion. Primary Books.
Tormey, R., Isaac, S. R., Hardebolle, C., & Le Duc, I. (2022). Facilitating experiential studying in greater training: Educating and supervising in labs, fieldwork, studios and tasks. Routledge/Taylor & Francis Group. https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/9781003107606

